Yield strength units 280111-Yield strength units imperial
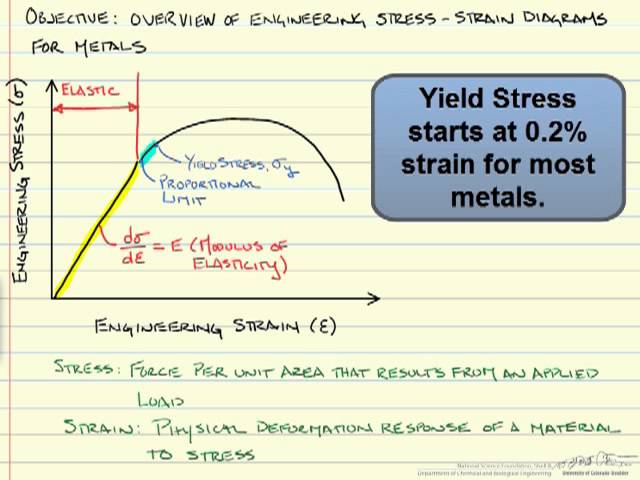
Yield strength σ y Yield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding a material deforms permanently;Measuring Yield Stress Approximate yield stress measurements can be gained by plotting the shear stress values for a range of shear rates, fitting a curve to the data, and extrapolating through the stress axis The intersect on the stress axis gives us our yield stress (figure 2)The minimum yield strength is the key property of steel used in pipeline design See Figure 1110This figure shows the relationship between stress and strain The minimum yield strength is defined as the tensile stress required to produce a total elongation of 05%
Nanohub Org Resources 6054 Download Ch07 Stress Strain Pdf
Yield strength units imperial
Yield strength units imperial-Unit of Strength of MaterialsFind typical requirement for ASTM A193 Grade Mechanical Properties for Metric and Imperial units All intermediary or finished products manufactured to ASTM a193 grade b7 specification must comply to tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, reduction or area and hardness as per below requirement


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf
Yield strength represents the upper limit of the load that can be safely applied to the metal, which makes it a very important number to know when designing components Elongation Ductility is the capability of the steel to be stretched out without becoming more brittle or weaker in the processThe specific strength is a material's strength (force per unit area at failure) divided by its density It is also known as the strengthtoweight ratio or strength/weight ratio In fiber or textile applications, tenacity is the usual measure of specific strength The SI unit for specific strength is (N/m2)/(kg/m3) or more commonly N·m/kgThe units used for Yield Strength are N/mm^2 (Newtons per millimeter squared), which is defined as the stress the material is able to resist before it yields (elongates without being able to return elastically)
Plates thicker than 8 in have a 32,000 psi (2 MPa) yield strength and the same ultimate tensile strength of 58,000–80,000 psi (400–550 MPa) The electrical resistance of A36 is 0142 μΩm at °C A36 bars and shapes maintain their ultimate strength up to 650 °F (343 °C)The Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformationYield Strength Yield strength of tool steel – steel depends on heat treatment process, but it is about 1400 MPa The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior
Yield Strength Yield strength of tool steel – steel depends on heat treatment process, but it is about 1400 MPa The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behaviorThe terms strength and stiffness often are used interchangeably, but they have different meanings and significance Strength Strength is a measure of the stress that can be applied to a material before it permanently deforms (yield strength) or breaks (tensile strength)The units are N/mm2 or MPa, the symbol is σbc ④ Yield Strength It refers to the stress of the metal sample during the stretching process, when the load no longer increases and the sample continues to deform The unit is N/mm2 or MPa symbol is σs The yield strength is the pressure value of the yield point


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
Once the yield strength of the plastic is attained, the material will not return to its original length and will yield Units are typically in Pascals (Pa) or pounds/inch (psi) Ultimate Strength – The ultimate strength is the maximum amount of stress that can be applied Units are typically in Pascals (Pa) or pounds/inch (psi)Small amounts of alloying elements are often added to copper to improve certain characteristics Alloying can increase or reduce the strength, hardness, electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, or change the color Common primary alloying elements include tin (resulting in bronze) or zinc (resulting in brass) VendorsDetermine the yield strengthtoweight density ratios (specific strength) in units of kN ∙m/kg for AISI 1018 CD steel, 11T6 aluminum, Ti6A14V titanium alloy, and ASTM No 40 gray cast iron



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion
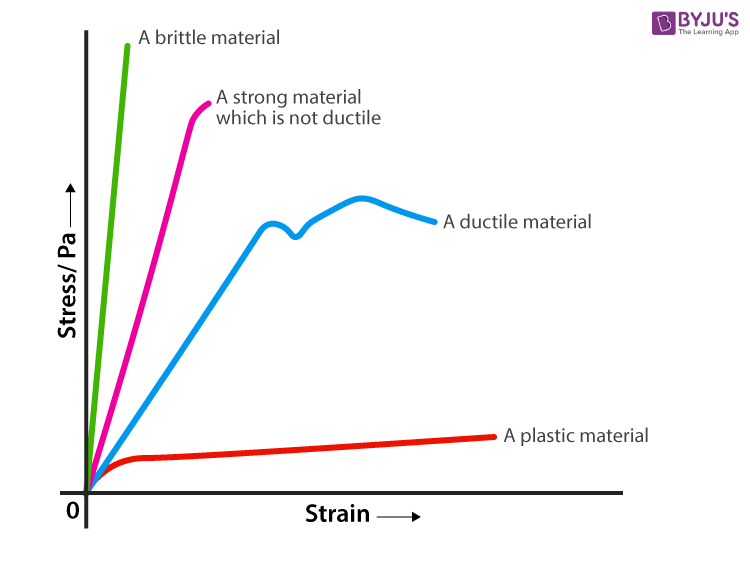


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
Then on the stressstrain diagram, lay off om equal to the specified value of the offset (ie yield strength ~02%), draw mn parallel to OA, and thus locate r, the intersection of mn with the stressstrain curve corresponding to load R, which is the yield strength load In recording values of yield strength obtained by this method, the valuePlates thicker than 8 in have a 32,000 psi (2 MPa) yield strength and the same ultimate tensile strength of 58,000–80,000 psi (400–550 MPa) The electrical resistance of A36 is 0142 μΩm at °C A36 bars and shapes maintain their ultimate strength up to 650 °F (343 °C)Once the yield strength of the plastic is attained, the material will not return to its original length and will yield Units are typically in Pascals (Pa) or pounds/inch (psi) Ultimate Strength – The ultimate strength is the maximum amount of stress that can be applied Units are typically in Pascals (Pa) or pounds/inch (psi)



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora
In Imperial units, stress can be measured in poundforce per square inch, which is abbreviated as psi Using the Pressure, Stress, Young's Modulus Converter Converter This online unit converter allows quick and accurate conversion between many units of measure, from one system to anotherFind typical requirement for ASTM A193 Grade Mechanical Properties for Metric and Imperial units All intermediary or finished products manufactured to ASTM a193 grade b7 specification must comply to tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, reduction or area and hardness as per below requirementFor example, aluminum has a yield strength of 14,000 pounds per square inch (or psi), copper has a yield strength of 10,000 psi, and steel, being an alloy of several different materials, has a



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Total Materia Article
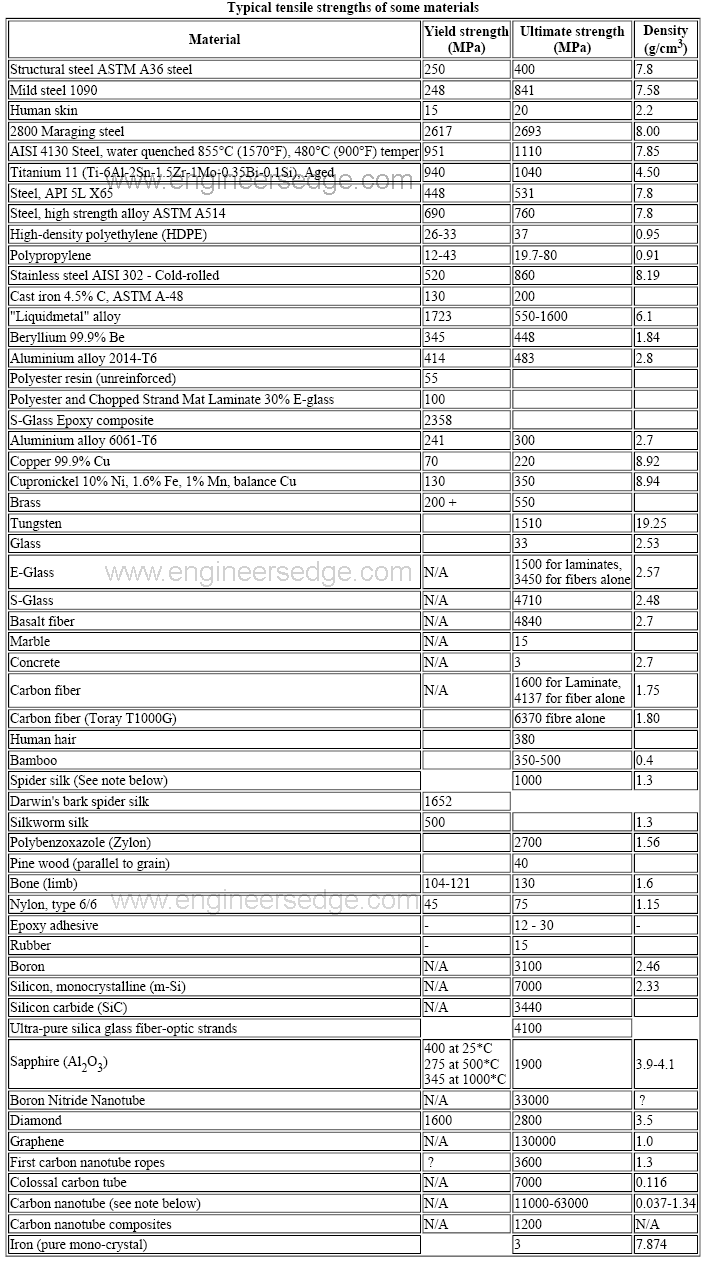


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
Measuring Yield Stress Approximate yield stress measurements can be gained by plotting the shear stress values for a range of shear rates, fitting a curve to the data, and extrapolating through the stress axis The intersect on the stress axis gives us our yield stress (figure 2)Copper is tough and ductile, but is valuable due its ability to conduct electricity While it is suited to many applications most centre around its excellent electrical conductivity (eg busbars and electric wire) Other uses utilise its corrosion resistance (eg water pipes and heat exchangers)Small amounts of alloying elements are often added to copper to improve certain characteristics Alloying can increase or reduce the strength, hardness, electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, or change the color Common primary alloying elements include tin (resulting in bronze) or zinc (resulting in brass) Vendors


3 032 Problem Set 6 Solutions


Civl 1101
Impact strength – also called impact toughness – is the amount of energy that a material can withstand when the said load is suddenly applied to it It may also be defined as the threshold of force per unit area before the material undergoes fracture 1 The s trength of materials may be defined in many ways, and some of the most common parameters include tensile strength, yield strengthPlates thicker than 8 in have a 32,000 psi (2 MPa) yield strength and the same ultimate tensile strength of 58,000–80,000 psi (400–550 MPa) The electrical resistance of A36 is 0142 μΩm at °C A36 bars and shapes maintain their ultimate strength up to 650 °F (343 °C)The units are N/mm2 or MPa, the symbol is σbc ④ Yield Strength It refers to the stress of the metal sample during the stretching process, when the load no longer increases and the sample continues to deform The unit is N/mm2 or MPa symbol is σs The yield strength is the pressure value of the yield point



What Is The Unit Of Measurement For The Tensile Strength Of Materials Carbon Fiber Aluminium Steel Plastics Etc Quora
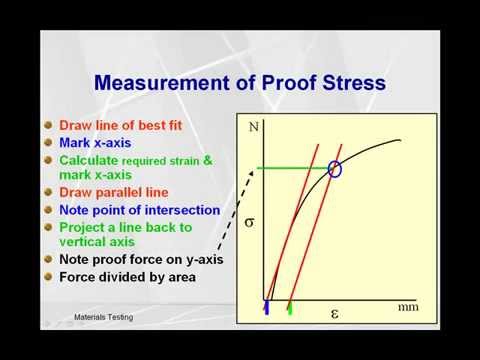


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube
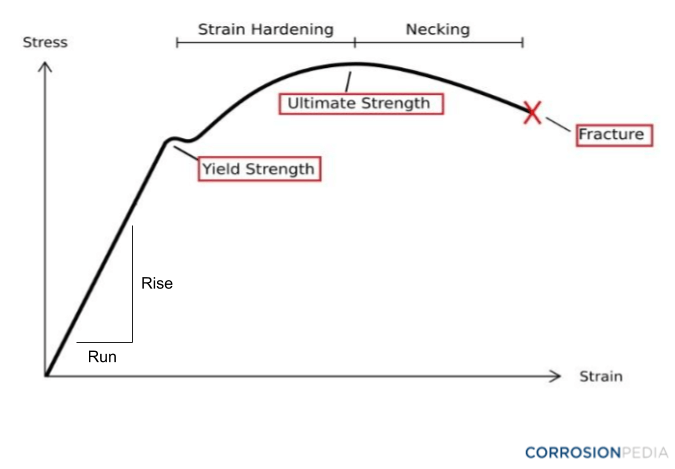
Ultimate tensile strengths vary from 50 MPa for an aluminum to as high as 3000 MPa for very highstrength steels Yield Strength Yield strength of cartridge brass – UNS C is about 95 MPa The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behaviorUltimate tensile strength (UTS) is considered as the failure criteria for brittle material In ductile materials, yield strength is much lower than ultimate strength For ductile materials, ultimate strength is roughly 15 times higher than yield strength Yield strength is used while designing components or structures made of ductile materialsThen on the stressstrain diagram, lay off om equal to the specified value of the offset (ie yield strength ~02%), draw mn parallel to OA, and thus locate r, the intersection of mn with the stressstrain curve corresponding to load R, which is the yield strength load In recording values of yield strength obtained by this method, the value



Ultimate Strength
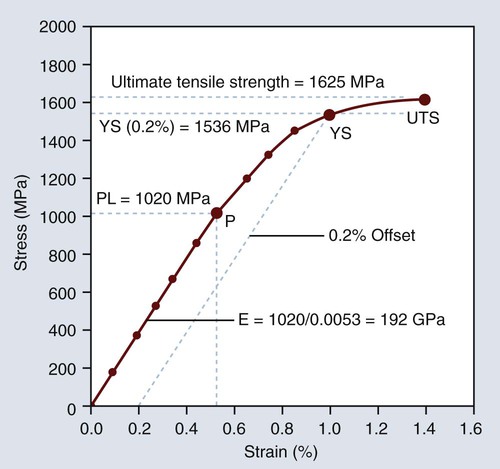


Mechanical Properties Of Dental Materials Pocket Dentistry
Use the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement) ksi MPa N/mm² psi = ksi MPa N/mm² psiG = d τ d γ = 2 π a b τ max {\displaystyle G= {\frac {d\tau } {d\gamma }}= {\frac {2\pi a} {b}}\tau _ {\max }} Giving a value of τ max {\displaystyle \tau _ {\max }} τ max equal to τ max = G b 2 π a {\displaystyle \tau _ {\max }= {\frac {Gb} {2\pi a}}} The theoretical yield strength can be approximated asMagmaweld Uluslararası Ticaret AŞ Bilim Sok Sun Plaza 5/7 Maslak İstanbul, Türkiye Mersis No



Does Unloading Beyond Yield Point Also Affect Tensile Strength Engineering Stack Exchange
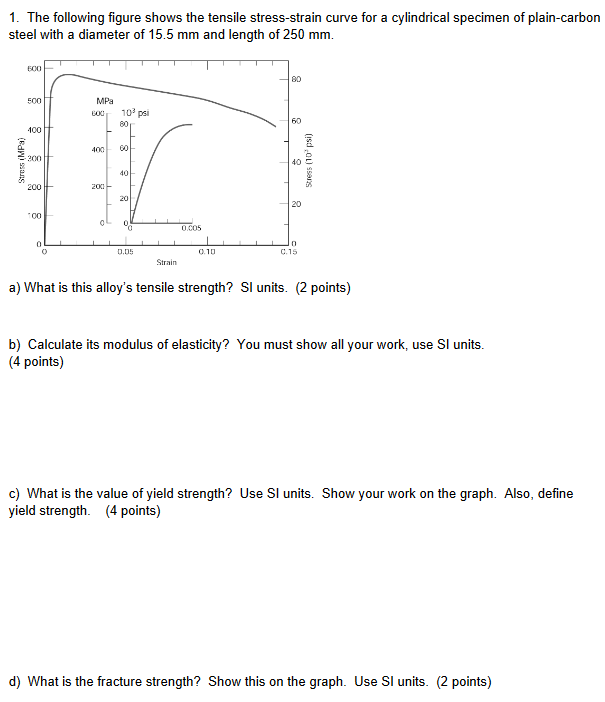


Solved 1 The Following Figure Shows The Tensile Stress S Chegg Com
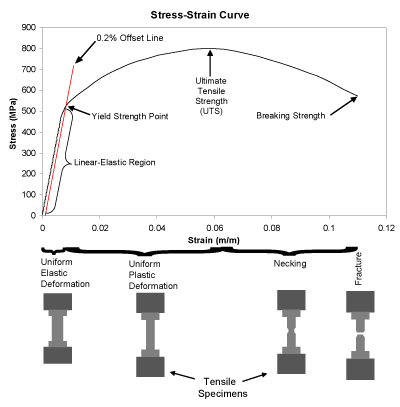
Yield strength is measured at the point of plastic deformation, while tensile strength is measured at the point of fracture Both yield strength and tensile strength are measured in N/m² or pascals Yield strength will always be lower than ultimate tensile strengthTable 3 Finally equation 2 was used to determine the cost per unit yield strength and cost per unit tensile strength, ie w Cost Cm σ ρ = (2) where Cm=cost per unit mass, ρ=density of the material and σw=safe working stress of the material 2 The safe working stress takes into account the factor of safety In the case of this experimentThe fracture strength is the point of strain (fracture point) where the material physically separates At this point, the strain reaches its maximum value and the material actually fractures, even though the corresponding stress may be less than the ultimate strength at this point



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Strain Ageing Of Steel Part One Total Materia Article
18/8 Stainless Steel Properties, Yield Strength, Composition, Density, Tensile Strength, Hardness Wiki By World Material 0 15,551 Share What is 18/8 Stainless Steel 18/8 stainless steel refers to the chemical composition of stainless steel containing 18% chromium (Cr) and 8% nickel (Ni)Yield strength is the stress needed to be applied to the specimen in order to reach the yield point For a given specimen, they are the same The only difference being yield strength is a property of the material, whereas yield stress is just the amount of stress induced What is the unit of strength?The tensile formula consists of stress Stress is measured in force, either in Newtons (N), Kilograms (KG), Pounds (Lbs), or other similar units over the cross sectional area of the material, generally Milimeters square (mm²) or square inches The
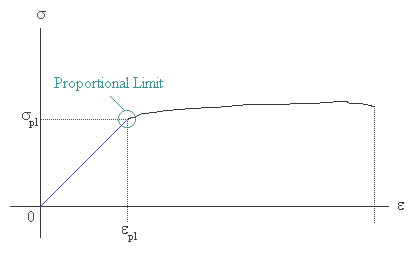


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia
Search is the most efficient way to navigate the Engineering ToolBox!Mechanical properties of aluminum alloys tensile strength, yield strength and more Engineering ToolBox Resources, Tools and Basic Information for Engineering and Design of Technical Applications!Impact strength – also called impact toughness – is the amount of energy that a material can withstand when the said load is suddenly applied to it It may also be defined as the threshold of force per unit area before the material undergoes fracture 1 The s trength of materials may be defined in many ways, and some of the most common parameters include tensile strength, yield strength


Http Www Csun Edu Bavarian Courses Mse 527 Tension Test Mse 527l Pdf
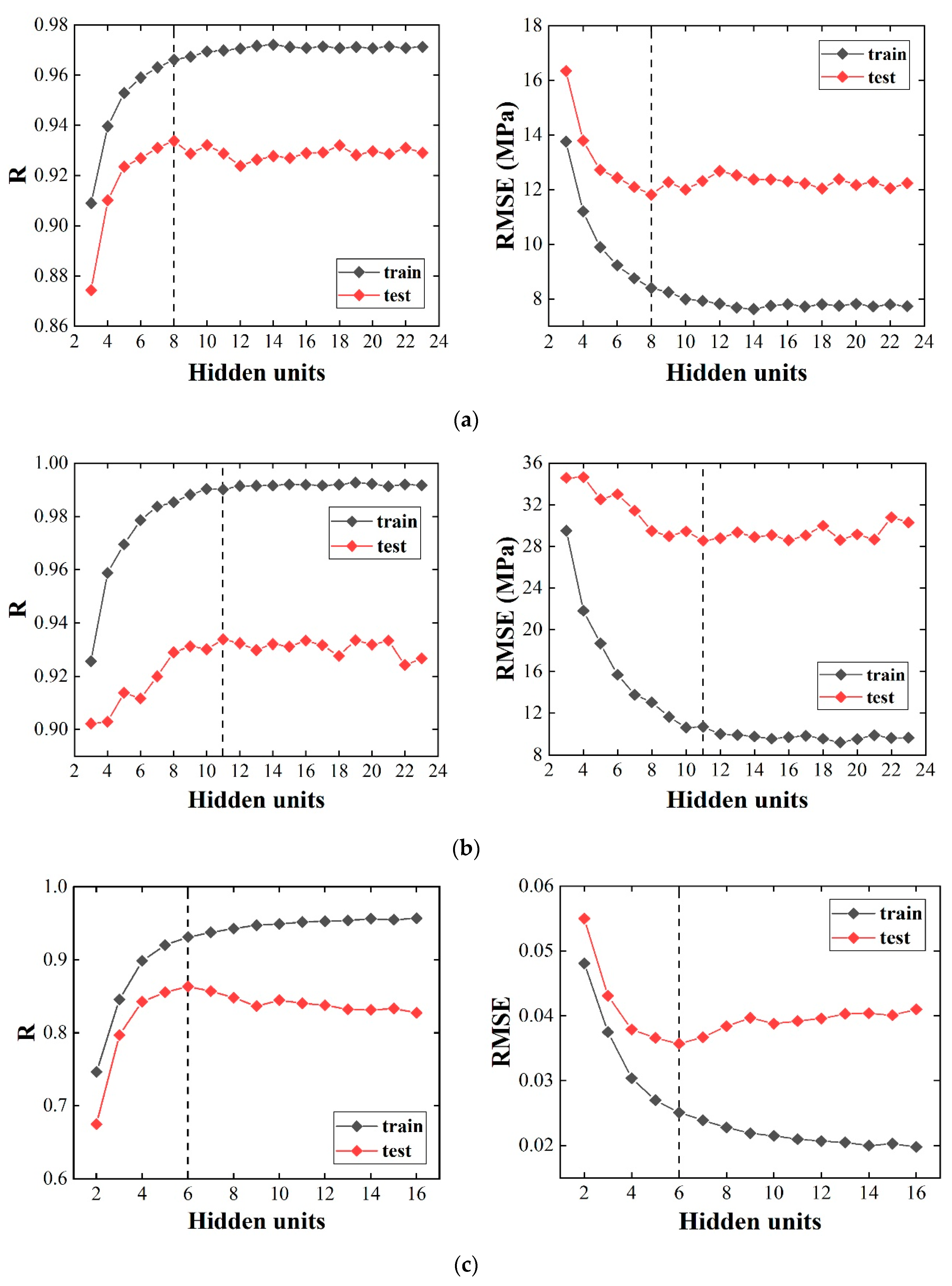


Metals Free Full Text Prediction And Analysis Of Tensile Properties Of Austenitic Stainless Steel Using Artificial Neural Network Html
Yield strength is mainly used there Another criterion might be based on the instances found in a google search "Yield strength" produces results, "yield stress" produces resultsYield Strength vs Tensile Strength Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingAs yield strength is related to deformation which is a result of applied stress, the SI unit of yield strength is Nm2 In CGS system, the yield strength is gcm2



Modulus Of Toughness Instron



Strength At Break Tensile
Yield strength is measured at the point of plastic deformation, while tensile strength is measured at the point of fracture Both yield strength and tensile strength are measured in N/m² or pascals Yield strength will always be lower than ultimate tensile strengthThe vector sum of the stresses due to forces and moments should not exceed the design strength P w A u = Unit Throat Area = (From table below) b d = (1 150) = 270mm 2 To obtain radius of Force from weld centre of gravity A = =223mm Moment M = Pr = = 2,2310 6 Nmm


What Is The Unit Of Measurement For The Tensile Strength Of Materials Carbon Fiber Aluminium Steel Plastics Etc Quora


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel


Q Tbn And9gctkrzf52tulw Hck4iec8kqmmvrheff2kzrugh6dmtmgku6pybl Usqp Cau


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials


Solved The Figure Shows The Stress Strain Curve For A Mat Chegg Com


Www Cheric Org Files Education Cyberlecture E1502 E1502 501 Pdf
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods



How To Find Yield Strength Quora


2


Nanohub Org Resources 6054 Download Ch07 Stress Strain Pdf



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


What Is A Tensile Modulus Definition From Corrosionpedia
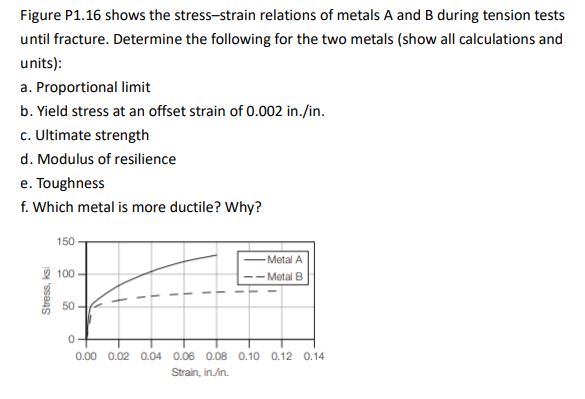


Answered Figure P1 16 Shows The Stress Strain Bartleby


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Yield Stress An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
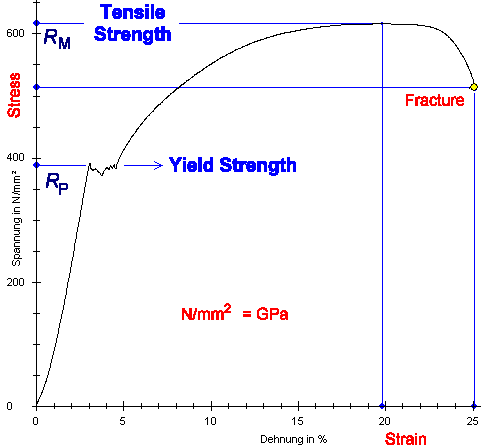


Science Of Uniaxial Deformation
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods


Property Information


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



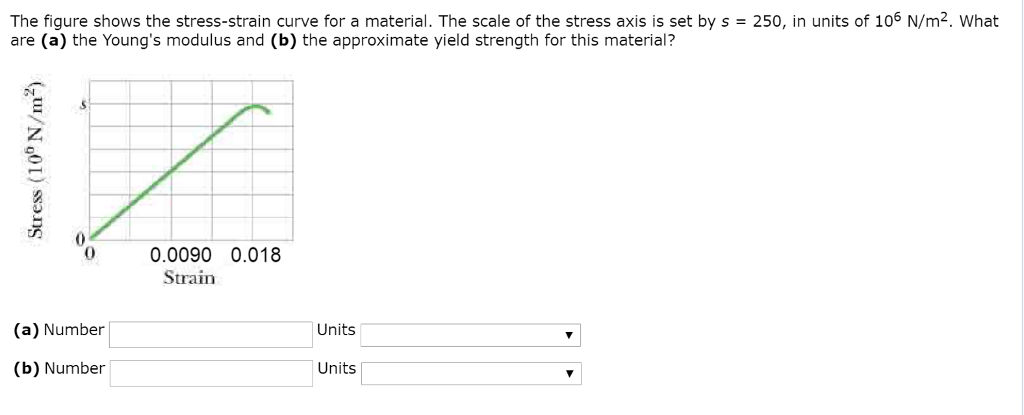
Figure Shows The Strain Stress Curve For A Given Material What Are A Young S Modulus And B Approximate Yield Strength For This Material


Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 Bf Pdf


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Quasi Non Destructive Evaluation Of Yield Strength Using Neural Networks


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau
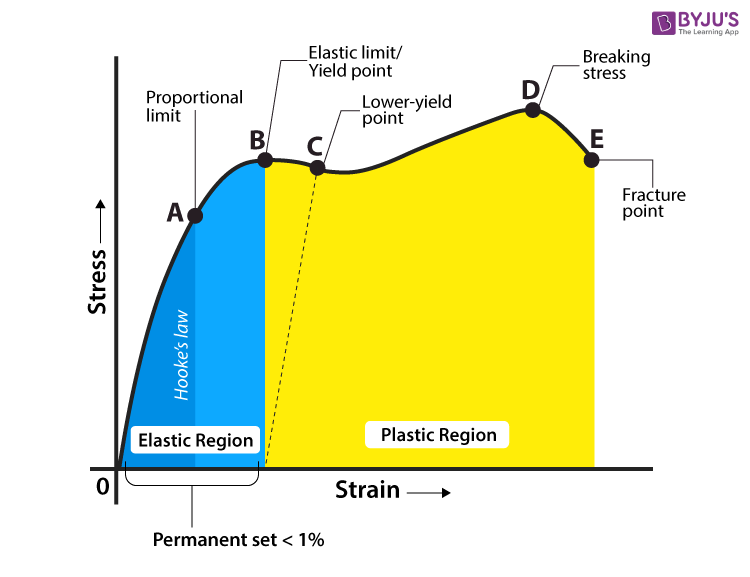


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Unit Of Strength Of Materials Nuclear Power Net
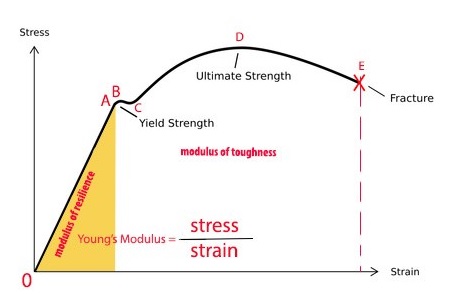


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations


What Are Tensile Strength Units Quora
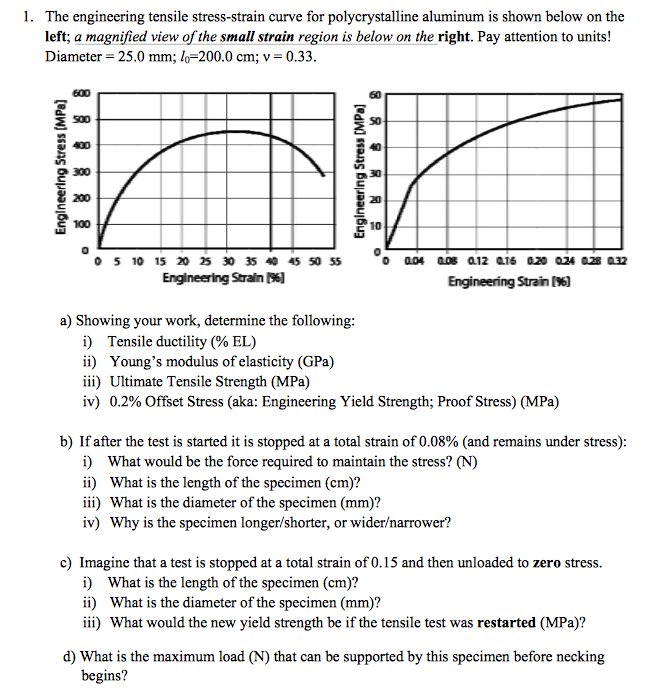


Solved The Engineering Tensile Stress Strain Curve For Po Chegg Com
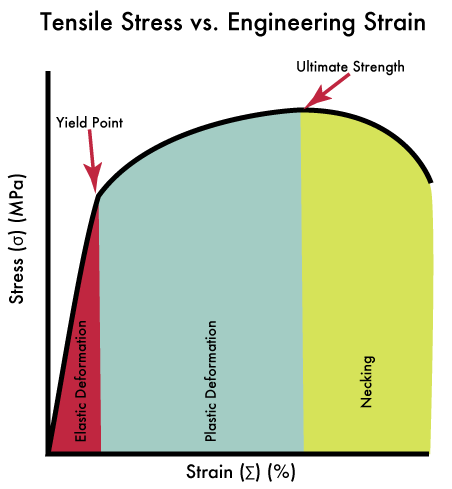


Mechanical Properties Of Sheet Metal Materials Complete List Machinemfg
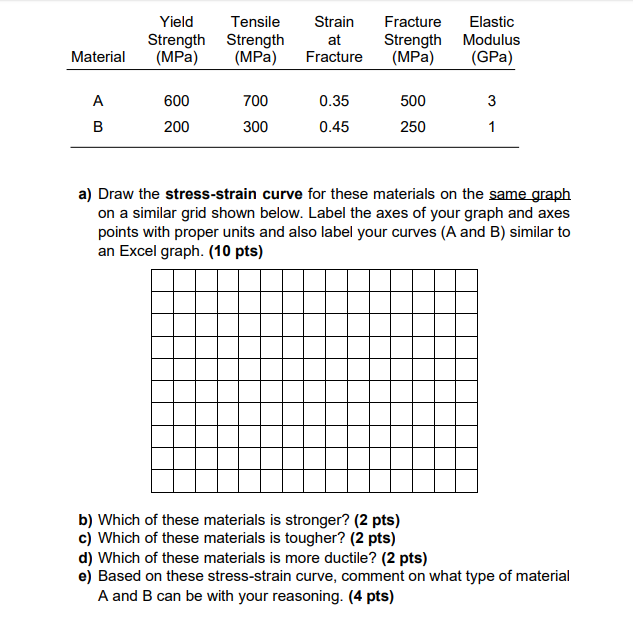


Solved Yield Strength Mpa Tensile Strength Mpa Strain Chegg Com
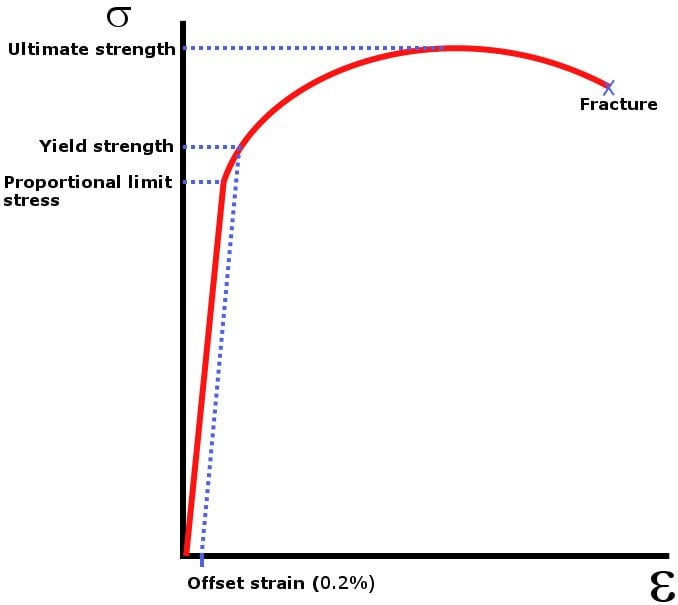


What Is Ultimate Tensile Strength Science Abc
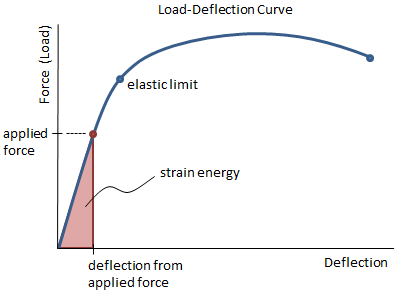


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Figure Shows The Strain Stress Curve For A Given Material What Are A Young S Modulus And B Approximate Yield Strength For This Material



Tensile Testing Principles Fundamentals Methods And Challenges 18 08 01 Quality Magazine



Yield Point And Gel Strength Petroleumroughnecks



What Is The Relation Between Tensile Strength And Young S Modulus Of A Material



Unit Of Strength Of Materials Nuclear Power Net



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
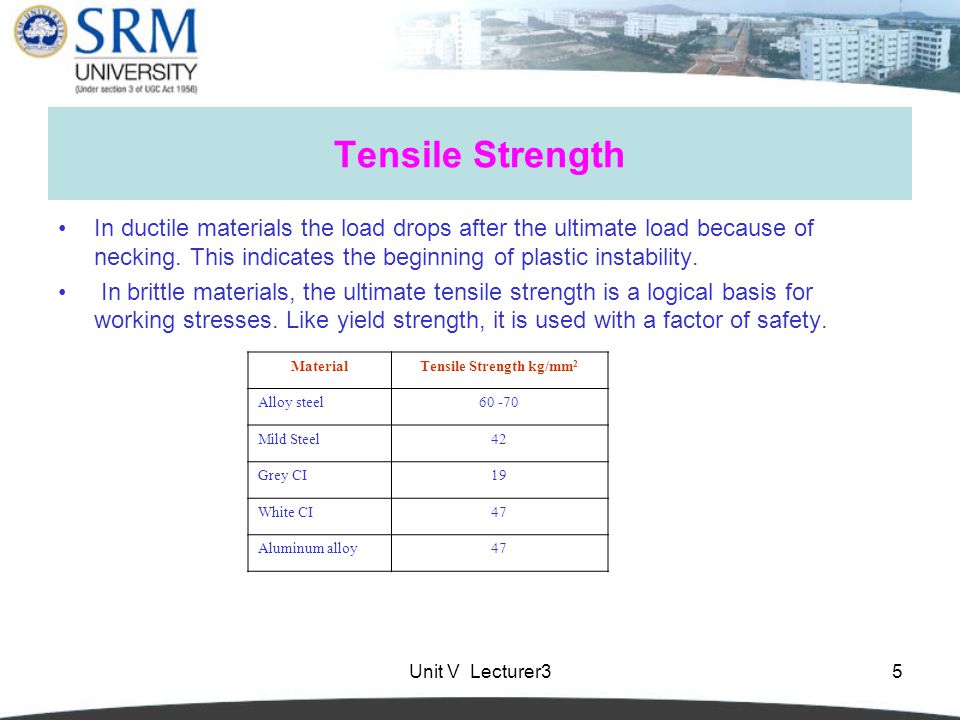


Lecturer 3 Fundamental Mechanical Properties I Tensile Strength Ppt Video Online Download


How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs



Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


Q Tbn And9gcqpjlgtnnmrjaszc Eg Tgaba Nvxolrhabne8f9t4 Gzo3vax Usqp Cau



Part 6 1 Ductility Toughness Resilience Hardness Deformation Engineering Ultimate Tensile Strength



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Strength At Break Tensile
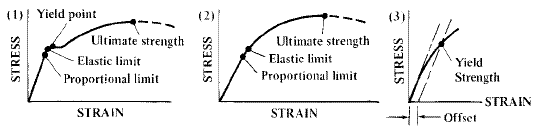


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf
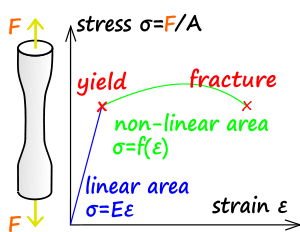


Strength Of Materials Wikipedia



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



M E S T E E L


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing



What Is Tensile Testing Instron


Young S Modulus Physics Forums


Property Information


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts
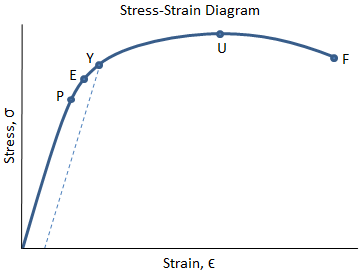


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
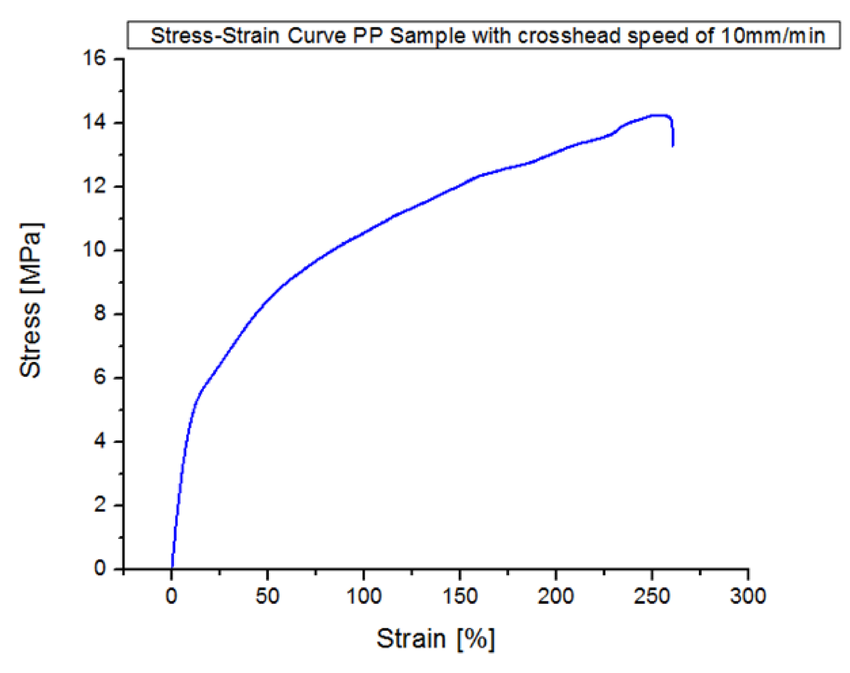


113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Poisson S Ratio N Poisson S Ratio N Units Ppt Video Online Download
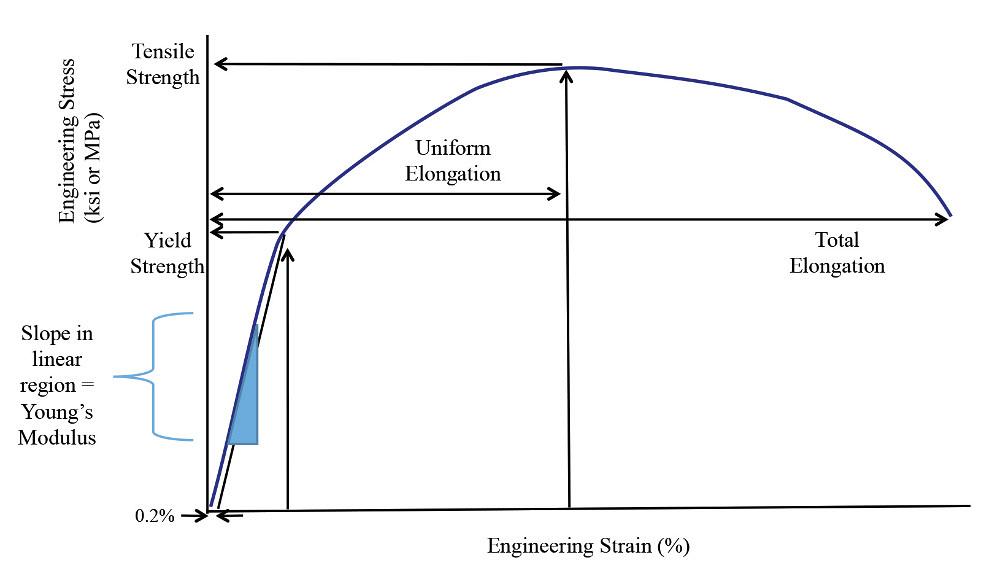


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming
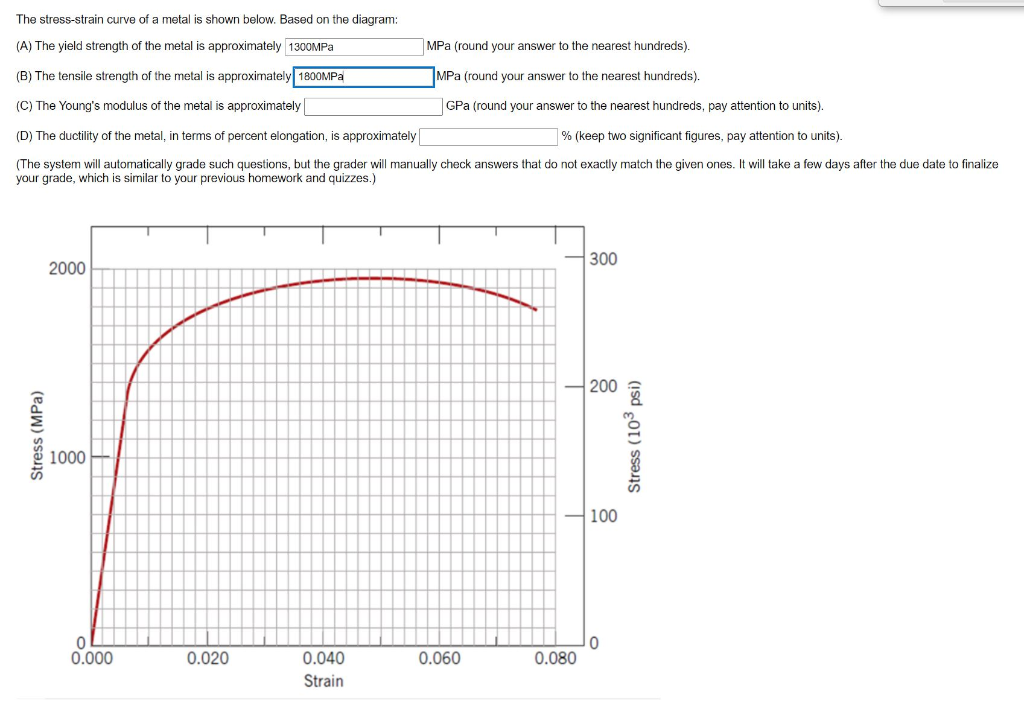


Solved The Stress Strain Curve Of A Metal Is Shown Below Chegg Com


Http People Virginia Edu Lz2n Mse9 Chapter6c Pdf


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau
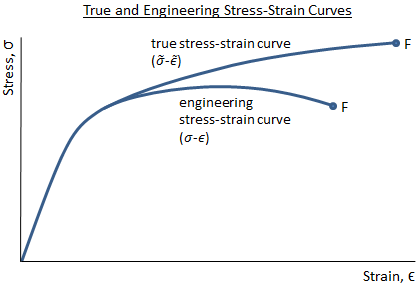


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Temperature And Strength Of Metals
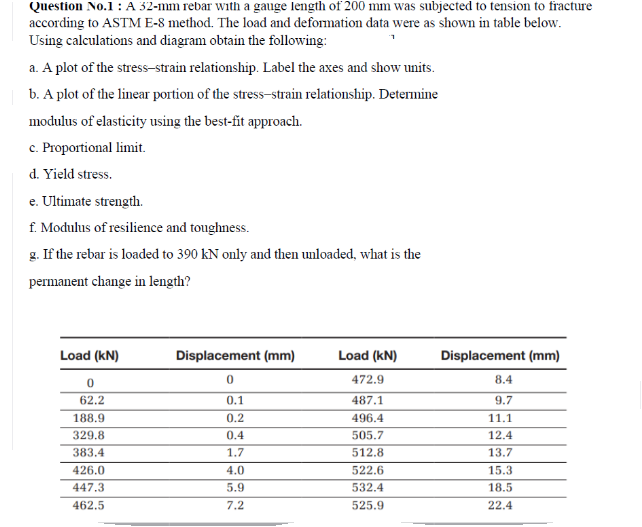


Answered Question No 1 A 32 Mm Rebar With A Bartleby
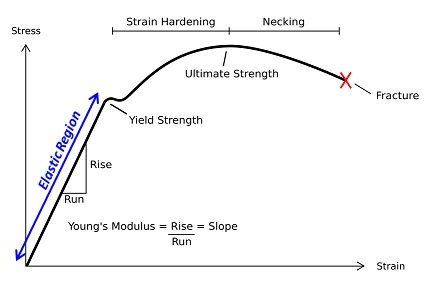


Mechanical Properties Of Sheet Metal Materials Complete List Machinemfg
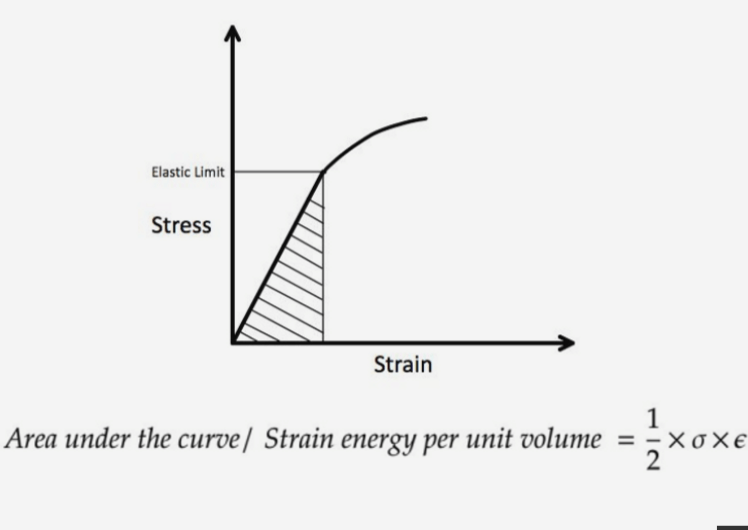


Modulus Of Resilience Definition Calculation 2 Examples



Strength At Break Tensile



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


コメント
コメントを投稿